 In Summer, 2015 we announced the beta launch of the cross-institutional archives portal College Women: Documenting the History of Women in Higher Education (collegewomen.org), a collaboration between the institutions once — and often still — known as the “Seven Sisters.” The site development was funded by a Foundations planning grant from the National Endowment for the Humanities, and allowed us to begin imagining a resource that could serve both researchers and the casual browser interested in the shared histories of women’s education at some of the first U.S. women’s colleges in the Northeast. Today, we can now share that the National Endowment for the Humanities has recently awarded a Humanities Collections and Reference Resources grant to Bryn Mawr College that will allow us to expand the digitization project with our seven partner institutions beginning in Summer 2016.
In Summer, 2015 we announced the beta launch of the cross-institutional archives portal College Women: Documenting the History of Women in Higher Education (collegewomen.org), a collaboration between the institutions once — and often still — known as the “Seven Sisters.” The site development was funded by a Foundations planning grant from the National Endowment for the Humanities, and allowed us to begin imagining a resource that could serve both researchers and the casual browser interested in the shared histories of women’s education at some of the first U.S. women’s colleges in the Northeast. Today, we can now share that the National Endowment for the Humanities has recently awarded a Humanities Collections and Reference Resources grant to Bryn Mawr College that will allow us to expand the digitization project with our seven partner institutions beginning in Summer 2016.
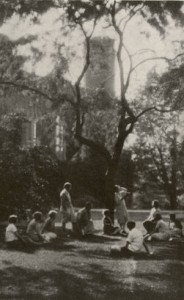
A Poetry Hour on Bryn Mawr’s Campus (1930) via collegewomen.org.
The College Women archives portal brings together digitized writings and photographs from our seven libraries, dating from the mid-nineteenth through the early twentieth centuries, and documenting the experiences of students attending Barnard, Bryn Mawr, Mount Holyoke, Smith, Vassar, Wellesley, and Radcliffe (now the Schlesinger Library, Radcliffe Institute for Advanced Study, Harvard University). In the first phase of our work, the partners established a metadata schema, built and tested the beta site, and developed an approach to building subject-focused digital collections that can serve as a model to other institutions pursuing collaborative ventures. The portal currently holds a sample selection of 318 items, mostly photographs; the next phase of the project will focus on the expansion of content, allowing us to digitize, catalog, and upload 50,000 new images to the portal with a focus on student writings from letters, diaries, and scrapbooks. The research value of these sources will be greatly increased by the ability to consider a wide range of student materials in conversation with each other, as part of a larger phenomenon in the history of women in America, rather than as isolated fragments that document only the history of the individual colleges.
In an era in which women’s access to education still cannot be taken for granted, and women’s colleges in the United States are increasingly pressured to justify their continued existence, the exposure of these unique collections will be a key resource for researchers interested in tracing the experiences and impact of women’s higher education. By linking these materials under a common searchable access point, we hope to illuminate questions that still resonate today: how did young women’s social and intellectual relationships inform their entry into the public sphere? How did differences in social and economic status between students influence day-to-day life on campus? How did the atmosphere of women’s education as nineteenth-century “experiment” influence their attitudes and experiences, both in their undergraduate years and beyond–and how might we use those histories to build supportive educational environments for marginalized populations around the world today?
Are you interested in using archival primary sources to explore the history of women’s higher education? Tell us what kinds of materials you would like to see included in CollegeWomen.org in the comments!
For more information, contact Eric Pumroy (epumroy [at] brynmawr [dot] edu) or Christiana Dobzynski (cdobrzynsk [at] brynmawr [dot] edu).